Every day, new technologies are altering how people live, work, and interact. From smart home devices to advances in artificial intelligence, these innovations are quietly becoming integral parts of daily routines. Emerging tech trends like AI, IoT, and 5G are reshaping everyday life by improving convenience, efficiency, and connectivity.
These trends influence various aspects, including communication, healthcare, and transport. For example, wearable health monitors provide real-time data, while autonomous vehicles promise safer roads. Understanding these developments helps people navigate a rapidly changing world with greater awareness and adaptability.
As technology evolves, its impact will grow deeper and more widespread. Staying informed about these emerging trends is essential for recognising how they may continue to transform everyday experiences in the near future.
Artificial Intelligence and Smart Integration
Artificial intelligence is increasingly embedded in daily life, improving convenience, efficiency, and user interaction. It enhances communication and decision-making by analysing data and automating tasks.
AI-Powered Virtual Assistants in Everyday Life
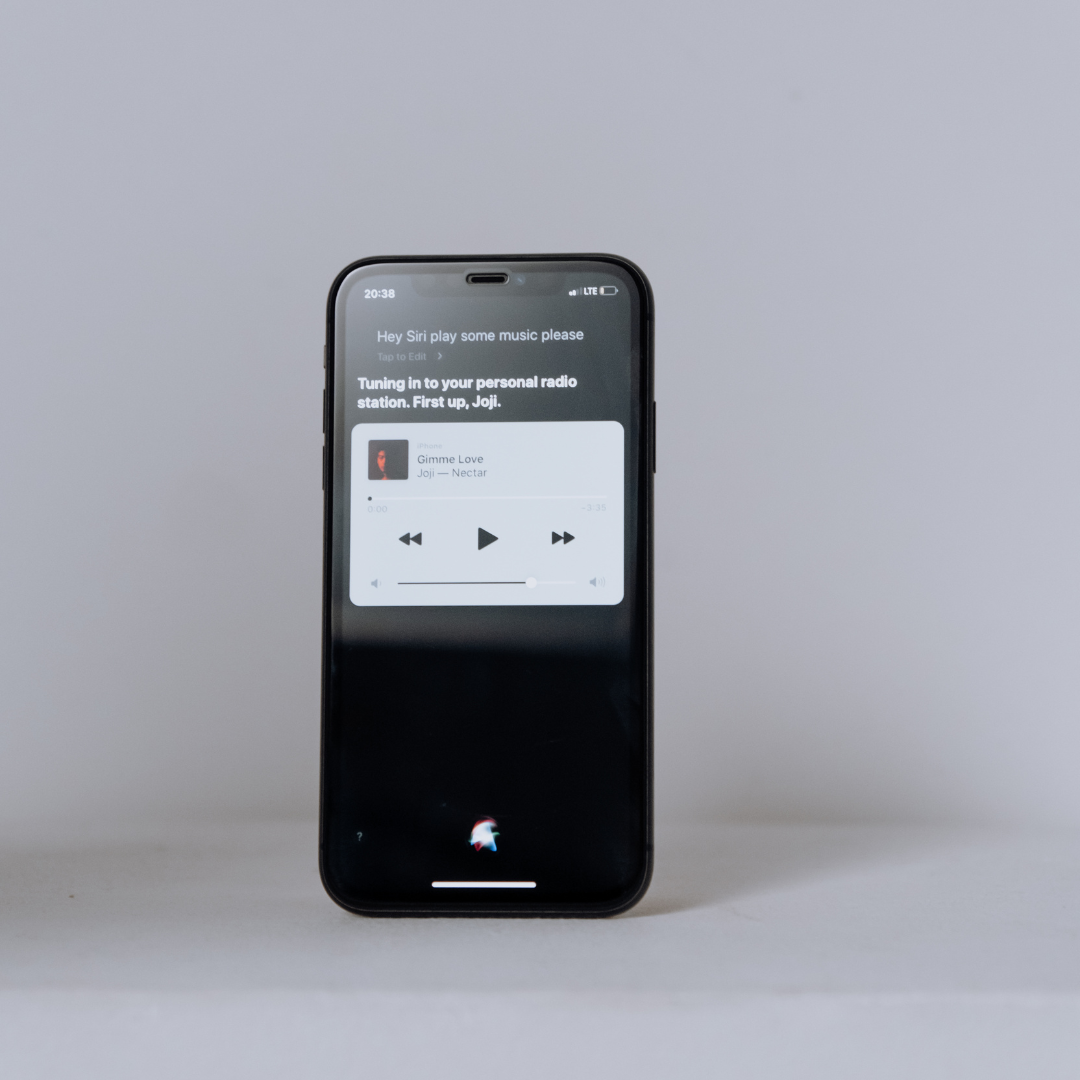
Virtual assistants like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant use AI to understand voice commands and perform tasks such as setting reminders, controlling smart home devices, and providing real-time information. These assistants improve over time by learning personal preferences and speech patterns.
They help manage schedules, send messages, and answer questions without manual input. Businesses also deploy chatbots powered by AI to handle customer service, reducing wait times and providing instant responses.
Personalisation Through Recommendation Engines
Recommendation engines analyse user behaviour, preferences, and past interactions to suggest products, services, or content tailored to individual tastes. Streaming platforms, online retailers, and news apps rely heavily on these AI algorithms to enhance user engagement.
Examples include personalised movie suggestions on Netflix or product recommendations on Amazon. These systems continuously update suggestions based on new data, creating a more relevant and efficient browsing experience that saves time and increases satisfaction.
Generative AI and Automated Content Creation
Generative AI technologies create text, images, and other media with minimal human intervention. This includes writing articles, generating marketing copy, and even producing artwork.
Content creators use tools powered by generative AI to automate repetitive tasks and speed up production. Marketers leverage this technology for personalised campaigns, enhancing reach and impact while reducing costs and time spent on content creation.
Connected Living: Internet of Things and Smart Homes
Connected living integrates everyday devices to improve convenience, energy use, and safety. Smart homes connect appliances and systems through the internet, allowing users to monitor and control them remotely. This technology is evolving to offer more personalised and seamless experiences.
Home Automation and Energy Efficiency
Smart thermostats and energy-efficient devices play a key role in reducing household energy consumption. These devices learn user preferences and adjust heating or cooling accordingly, cutting unnecessary energy use. For example, a smart thermostat can lower the temperature when no one is home, then warm the space again before arrival.
Smart fridges now offer monitoring of food stocks and can suggest recipes, contributing indirectly to less waste. Automated lighting systems switch off lights in unused rooms, further conserving electricity. Together, these technologies make homes more eco-friendly while lowering utility bills.
Wearable Devices and Health Monitoring
Wearable devices track vital signs such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity in real time. They support individuals managing chronic conditions by alerting users and healthcare providers to potential health issues early.
Many wearables integrate with smart home systems to adapt environments based on health data. For example, lighting can be adjusted to improve sleep cycles, or activity reminders can be sent through connected speakers. This integration enhances personal well-being through continuous data monitoring.
Smart Security Systems for Enhanced Safety
Modern security systems use connected sensors, cameras, and alarms to provide real-time alerts. They allow homeowners to monitor property remotely via apps, enabling instant responses to suspicious activity.
Features include motion detection, facial recognition, and automated door locking. Integration with other smart home devices ensures that security measures cooperate seamlessly, such as turning on lights when detecting movement. This approach significantly strengthens household safety.
Immersive Experiences: AR, VR, and 5G Connectivity
Immersive technologies are transforming how people interact with content and environments. The integration of augmented reality, virtual reality, and faster 5G connections is expanding the scope of education, entertainment, retail, and real-time digital services.
Augmented Reality in Education and Retail
Augmented reality (AR) is increasingly used to enhance learning by layering digital information onto real-world settings. In education, AR enables students to visualise complex concepts through interactive 3D models. This hands-on approach can improve engagement and retention, particularly in science and technical subjects.
Retail sectors use AR to allow customers to preview products in their own environment before purchasing. For example, AR apps let users “try on” clothes virtually or see how furniture fits in their homes. These applications reduce return rates and improve customer satisfaction by providing a clearer sense of the product.
Virtual Reality for Entertainment and Training
Virtual reality (VR) offers immersive environments for entertainment, allowing users to experience games, movies, or virtual tours in a fully engaging way. VR headsets create a sense of presence, making entertainment content more interactive and lifelike.
In training, VR creates safe, controlled simulations for fields such as healthcare, aviation, and manufacturing. Trainees can rehearse procedures or operate machinery in virtual settings, reducing risks and costs compared to real-world practice. This technology also enables remote training, broadening accessibility.
5G Networks Enabling Real-Time Digital Interactions
5G connectivity delivers much higher speeds, lower latency, and more reliable network coverage than previous generations. This enhancement supports seamless real-time interactions between devices, which is crucial for immersive technologies like AR and VR.
Industries benefit from 5G by enabling better mobile broadband, enhanced remote collaboration, and more precise data streaming. The network’s architecture supports the growing demand for connected devices and real-time service delivery, improving the responsiveness and quality of user experiences.
Real-Time Gaming and Streaming Platforms
Real-time gaming relies heavily on low-latency connections, which 5G networks can provide. This enables multiplayer games to run smoothly, with minimal lag, and supports cloud gaming services where processing takes place on remote servers.
Streaming platforms also gain from 5G by allowing higher-resolution content to be delivered without buffering. Users can access live streams, VR content, and interactive media on mobile devices anywhere, expanding entertainment possibilities beyond traditional fixed broadband constraints.
Digital Security, Blockchain, and Sustainable Innovations
Digital security continues to evolve alongside blockchain technology and sustainable materials, driving changes in finance, data protection, and environmental impact. These areas converge to create more transparent, secure, and eco-conscious solutions.
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology extends far beyond cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It provides a secure, decentralised ledger that ensures the integrity of data across various applications, including supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems.
Businesses use immutable records to verify authenticity and improve traceability, reducing fraud and inefficiencies. Smart contracts automate agreements by executing terms when conditions are met, lowering reliance on intermediaries.
The transparency inherent in blockchain supports regulatory compliance, increasing trust between parties. This application is crucial for sectors demanding accountability and auditability, not just financial transactions.
Web3 and Decentralised Finance
Web3 represents the next internet phase, built on decentralised protocols that return control to users. It enables decentralised finance (DeFi), which removes traditional financial intermediaries by using blockchain-based platforms.
DeFi offers peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and asset exchange through smart contracts. This lowers costs and expands access to financial services, especially in underbanked regions.
Users interact directly with cryptocurrencies and stablecoins within these ecosystems, increasing financial inclusivity. However, smart contract security remains vital to prevent vulnerabilities and exploitation.
Advancements in Data Security and Authentication
Data security is increasingly focused on enhancing authentication methods to protect sensitive information. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometrics, and blockchain-based identity verification are gaining traction.
Blockchain’s decentralised nature offers resistance to hacking by distributing data across nodes, reducing single points of failure. This is particularly important for securing identities and transactions.
Improvements in encryption and zero-knowledge proofs allow organisations to verify information without revealing the data itself. Such techniques strengthen privacy while maintaining integrity during digital interactions.
Sustainable Tech and Biodegradable Materials
Sustainable technology is advancing through biodegradable electronics and eco-friendly materials that reduce e-waste. These innovations address environmental concerns associated with traditional tech production and disposal.
Materials like biodegradable polymers and plant-based composites are being integrated into device manufacturing to lessen plastic pollution. Companies focus on energy-efficient components and circular economy principles.
Sustainable tech also includes blockchain solutions that track material provenance and lifecycle, helping businesses verify sustainable sourcing. This intersection of tech and ecology fosters responsible consumer products and industrial processes.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.